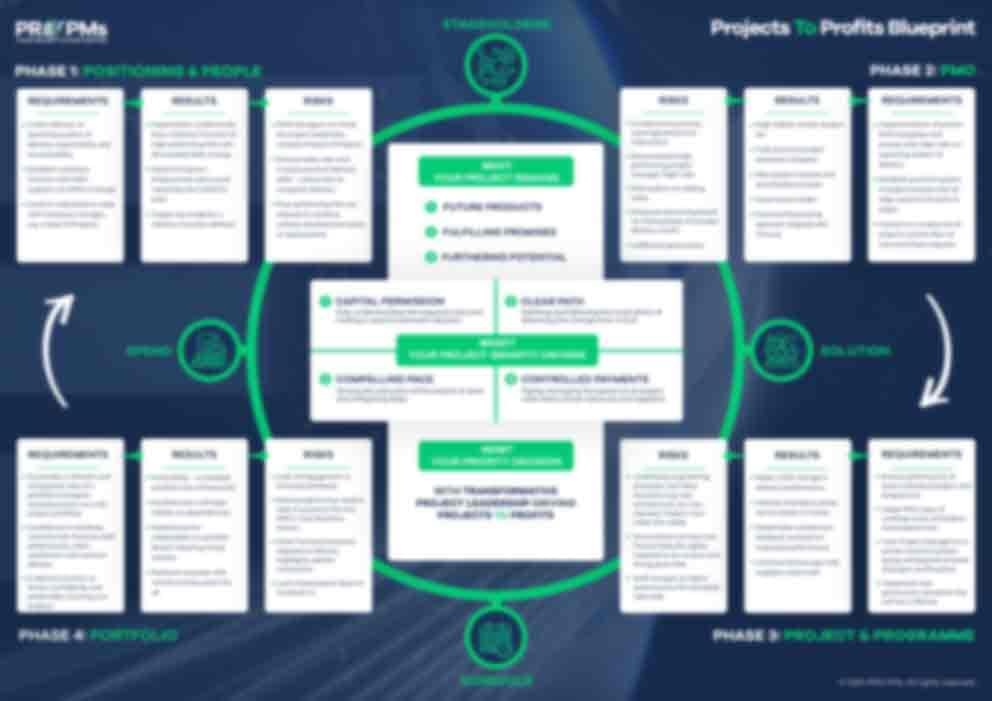
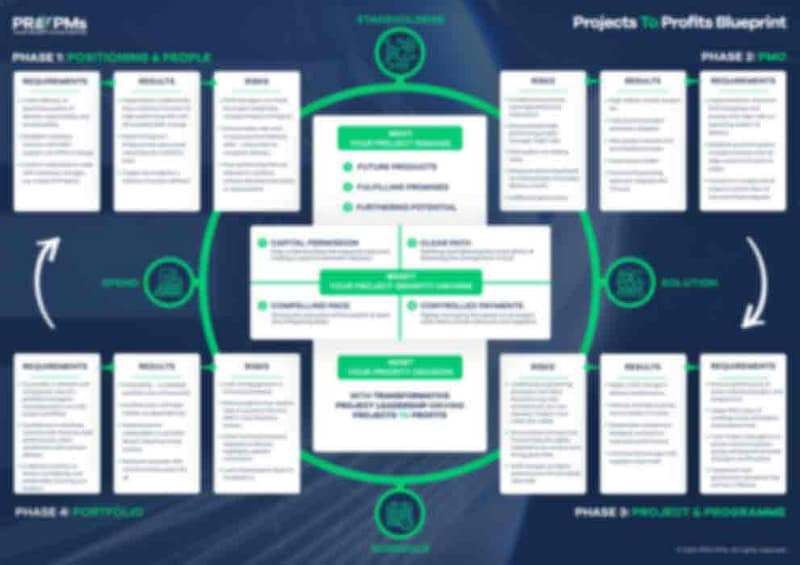
In today’s fast-paced business environment, the difference between project success and failure often comes down to one critical factor: when and how organizations approach testing. The traditional model of saving testing for the final phase is not just outdated—it’s a recipe for costly surprises and project delays.
Moving Beyond the Testing Phase Mentality
The most successful organizations have fundamentally shifted their approach to quality assurance. Instead of treating testing as a discrete phase that happens after development, they’ve embraced a testing mindset project management approach that permeates every aspect of their project lifecycle.
This transformation isn’t just about changing processes—it’s about changing how teams think about quality. When testing becomes a mindset rather than a milestone, organizations begin to see quality as something that’s built in, not bolted on.
The Power of Early Stage Project Testing
Consider how Microsoft’s new Windows AI Labs program exemplifies this approach. Rather than waiting until features are fully developed, Microsoft is testing experimental AI-powered features early in the development cycle. This allows them to gather feedback, identify issues, and make adjustments when changes are still relatively inexpensive to implement.
Similarly, Dell’s ‘Project Maverick’ demonstrates how organizations can systematically test and transform their internal systems for future readiness. By building testing into their transformation strategy from the beginning, they’re positioning themselves to adapt confidently to AI-driven changes.
Early testing project lifecycle implementation typically includes:
- Testing assumptions during the planning phase through stakeholder interviews and market research
- Validating designs through user testing and prototype feedback before full development begins
- Conducting integration testing throughout development rather than waiting for deployment
- Creating continuous feedback loops that identify issues when they’re cheapest to fix
Creating Effective Feedback Loops for Project Delivery
The key to successful systematic testing approach lies in establishing robust feedback loops at every project stage. These loops serve as early warning systems, catching potential problems before they become expensive fixes or project-threatening issues.
Effective feedback loops project delivery include:
- Planning Phase Testing: Before committing resources, test your project assumptions through stakeholder validation, market research, and feasibility studies
- Design Phase Validation: Use prototypes, mockups, and user testing to validate solutions before investing in full development
- Development Integration: Implement continuous integration practices that test code changes as they’re made, not after they’re complete
- Pre-Deployment Verification: Conduct thorough integration testing before deployment to ensure all components work together seamlessly
The Economics of Continuous vs Episodic Testing
The financial impact of adopting a continuous testing methodology versus traditional episodic testing is significant. Research consistently shows that fixing defects early in the project lifecycle costs exponentially less than addressing them later.
When organizations implement quality built into process approaches, they typically see:
- Reduced rework and project delays
- Lower overall project costs due to early issue identification
- Improved stakeholder confidence and satisfaction
- More predictable project outcomes and delivery timelines
This shift from continuous vs episodic testing fundamentally changes how teams approach quality assurance. Instead of hoping everything will work when pieces come together, teams gain confidence through systematic validation at each step.
Building Predictable Quality Delivery
Organizations that master testing at every project stage create what we call predictable quality delivery. This means quality becomes an expected outcome rather than a pleasant surprise.
The path to predictable quality involves:
- Standardizing Testing Practices: Develop consistent approaches to testing that can be applied across different project types and teams
- Training Teams in Testing Mindset: Ensure all team members understand their role in maintaining quality throughout the project lifecycle
- Implementing Quality Gates: Create specific checkpoints where projects must meet quality criteria before proceeding to the next phase
- Measuring and Improving: Track quality metrics throughout the project and use these insights to continuously improve your testing approach
Implementing Testing-Driven Project Success
Achieving testing driven project success requires more than just good intentions—it requires systematic implementation and organizational commitment. Start by evaluating your current quality assurance project lifecycle and identifying opportunities for earlier intervention.
Begin with small experiments: introduce user testing in your design phase, implement daily integration testing, or start conducting assumption validation workshops during project planning. As teams see the benefits of early testing, they’ll naturally embrace the broader testing mindset.
The goal is to reach a point where your organization delivers with confidence through systematic testing. When teams know their solutions have been validated at every step, they can focus on execution rather than hoping everything will work as intended.
The Future of Quality-First Project Management
As technology continues to evolve rapidly, organizations that embed testing throughout their project lifecycle will have a significant competitive advantage. They’ll be able to adapt quickly, deliver reliably, and maintain stakeholder confidence even in uncertain environments.
The question isn’t whether your organization should adopt a continuous testing methodology—it’s how quickly you can implement it. In a world where project success depends on quality delivery, testing isn’t just a phase you go through—it’s the mindset that gets you there.
Ready to transform your project delivery approach? Start by examining where systematic testing begins in your current project lifecycle, then work to push that starting point earlier and earlier until testing becomes truly continuous throughout your process.